Starting with these theories can provide the context and perspective necessary to better appreciate other sociological theories of crime. Deviance defines moral boundaries people learn right from wrong by defining people as deviant.

Self Identity Personal Identity Identity Personal Achievements
Four of the most wellknown follow.
. Among the pathways that she identified as crucial to understanding persistence is. Our values beliefs goals and identities are developed in the. Structural Functionalism Social Strain Typology Conflict Theory and Labeling Theory.
Conformists pursue their goals to the extent that they can through. Begins with minor underhanded behavior that leads to property damage and eventually escalates to more serious forms of criminality There are some neurological differences between males and females. Psychoanalytic theory which was developed by Sigmund Freud states that all humans have natural drives and urges that are repressed in the unconscious.
How Psychoanalytic Theory Explains Deviance. So if individuals are socially labeled as thugs or gangsters this label then encourages them to behave in ways. The Labelling Theory of Crime.
The Essential Nature of Deviance Émile Durkheim believed that deviance is a necessary part of a successful society. Anomie Anomie The concept anomie was used by early sociologists to describe changes in society produced by the Industrial Revolution. Females are _____-brain oriented while males are _____-brain oriented.
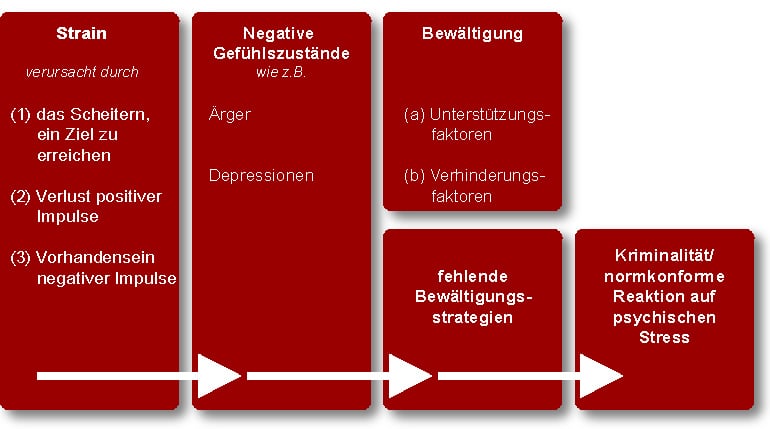
Mertons Strain Theory of Deviance. A child that is improperly. Innovators pursue goals they cannot reach through legitimate means by instead using criminal or deviant.
Merton asserted that societies are composed of two core aspects. Culture and social structure. American sociologist Robert Mertons theory of anomie holds that deviance is often a response to situations in which goals cannot be achieved through conventional behaviour.
Types of Deviant Paths. Strain theory social disorganization theory and cultural deviance theory represent three functionalist perspectives on deviance in society. Strain Theory argues that crime occurs when there arent enough legitimate opportunities for people to achieve the normal success goals of a society.
A the role of cumulative exposure to stressors lifetime exposure to stressors can shape contemporary response to stressors in a number of ways including depletion of coping resources and shaping cognitive strategies to respond to stressor exposure in deviant ways. Which of the following choices best describes the covert pathway. Strain TheoryAnomie Theory of Deviance Conformity.
Those who conform choose not to deviate. Deviance pushes societys moral boundaries which in turn leads to social change. Merton developed strain theory a concept connected to both the functionalist perspective on deviance and Émile Durkheims theory of anomie.
According to this theory the environment plays a major role in deciding which norms people. Crime is a result of a strain between legitimate goals and lack of opportunities to achieve those goals. When a person accepts both goals and means the result is conformity.
When social deviance is committed the collective conscience is offended. These tendencies are curbed however through the process of socialization. Merton s theory states that deviance is most likely to occur when there is a gap between culturally desirable goals such as money and material goods and a legitimate way of obtaining them.
But Ill do my best to list the main theories of crime and deviance. The labeling theory of deviance is influenced by symbolic interaction. While there are many different sociological theories about crime there are four primary perspectives about deviance.
Additionally all humans have criminal tendencies. D Deviance is socially defined. The labelling Theory of Crime is associated with Interactionism the Key ideas are that crime is socially constructed agents of social control label the powerless as deviant and.
Labeling theory tries to explain deviant behavior by suggesting that people given a negative or deviant label by society can be influenced by that label. The first school of thought of criminology headed by Beccaria states that people are rational we weigh cost and benefit and we make decisions on how to act based on which one outweighs the other for a given action. Classic Strain Theory predicts that deviance is likely to happen when there is a misalignment between the cultural goals of a society such as monetary wealth and the opportunities people have to obtain them.
B Deviances definition is determined by ones religion. In such a situation there is a strain between the goals and the. Structural-functionalism symbolic interaction and the creation of social conflict are theoretical approaches for understanding deviance.
A high school teacher who simply goes through the motions of teaching classes without any thought of success is an example of which response in strain theory. This approach may also signify that the cause of crime may be linked to inequalities of race class and gender. A serious form of deviance forces people to come together and react in the same way against it.
Which of the following best describes how deviance is defined. Labelling theory argues that criminal and deviant acts are a result of labelling by authorities and the powerless are more likely to be negatively labelled. In democratic societies people from wealthy highly connected and privileged circumstances have relatively easy routes to personal success and prosperity.
Charlene is experiencing what sociologists Clifford Shaw and Henry McKay called cultural deviance theoryThe theory states that the individual is not responsible for. Society set forth goals for the individuals to aim at and also laydown means to achieve them. The conflict theory links deviance to the power of norms and the imagery of the rich and powerful which the law society supports.
American sociologist Robert K. Sutherlands theory of differential association was one of the most influential sociological theories ever. According to Mertons strain theory societal structures can pressure individuals into committing crimes.
C Deviance occurs whenever someone else is harmed by an action. Cultural Deviance Theory. The four deviant responses represent reactions to the strain people feel between the goals they want and their access to the institutionalized means to reach them.
This is supported by the conflict theory which shows how deviance reflects on inequalities and power. A number of theories related to deviance and criminology have emerged within the past 50 years or so. A single and simple conception of theory is unlikely to apply across all fields fr Deviance The term deviance usually refers to some behavior.
The earlier in our life that we associate with deviant individuals and the more often we do so the more likely we become deviant ourselves. A Deviance is defined by federal state and local laws. In this way a normal social process socialization can lead normal people to commit deviance.
Edwin Sutherland coined the phrase differential association to address the issue of how people learn deviance. The demise of traditio Theory Theory The notion of a theory is controversial in social science.


0 Comments